Installing rsyslog
- First, make sure the rsyslog service is installed:
sudo dnf install rsyslog -y
![]()
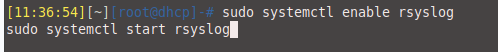
- Once installed, activate and start the service:
sudo systemctl enable rsyslog sudo systemctl start rsyslog
rsyslog server configuration
- Enable reception of remote logs
Let’s edit the main rsyslog configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/rsyslog.conf
![]()
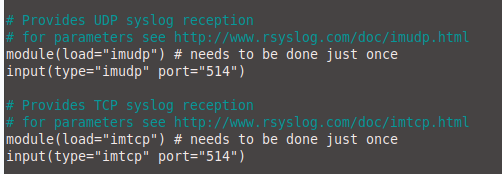
Make sure to uncomment or add the following lines:
# Allow reception by UDP module(load="imudp") input(type="imudp" port="514") # Allow reception by TCP module(load="imtcp") input(type="imtcp" port="514")
- Configuration to save separate logs per host
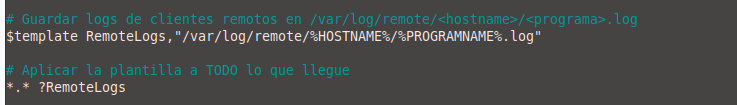
We also add to the end of the file:
# Template for organizing remote logs
$template RemoteLogs,"/var/log/remote/%HOSTNAME%/%PROGRAMNAME%.log"
# Apply the template to all received logs
*.* ?RemoteLogs
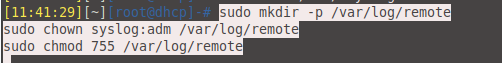
- Create folder for remote logs
sudo mkdir -p /var/log/remote sudo chown syslog:adm /var/log/remote sudo chmod 755 /var/log/remote
- Firewall settings
Make sure the server accepts connections on port 514 (both TCP and UDP):
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=514/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=514/udp sudo firewall-cmd --reload

-
Restart the rsyslog service
Once the modifications are done:
sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
![]()
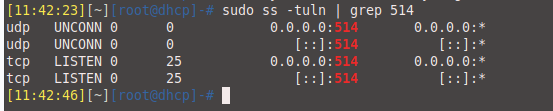
- Configuration verification
Make sure port 514 is listening:
sudo ss -tuln | grep 514
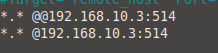
- on another machine in config document sudo nano /etc/rsyslog.conf we put:
sudo nano /etc/rsyslog.conf
TRIAL:
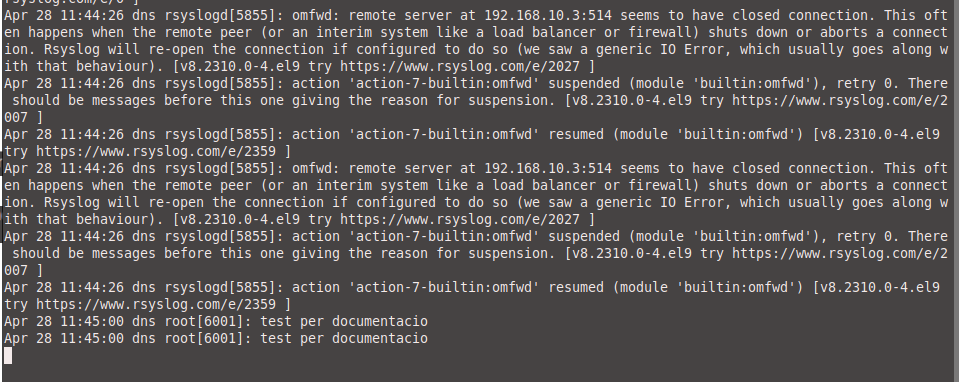
log from the machine:
![]()
server:
![]()